KonTActs Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
- This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project created by the SE-EDU initiative.
- We took references from OpenCSV for import and export commands.
- ChatGPT was used to check for errors and generate some test cases.
- It was used to generate the first two test cases in RemoveGradeCommandParserTest.java, MarkCommandParserTest.java & MarkCommandTest.java.
- It was also used for the usage of
.getStyleClass()&.add()methods in PersonCard.java to display the information clearly. - It was consulted to get a plan of how
PersonComparatorcan be implemented. - It was consulted to fix and improve the UI.
- We referred to our TA (Wu Xiaoyun) team's usage of "newPage" and "newPageBetween" here to set our pagination for the User and Developer Guide.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
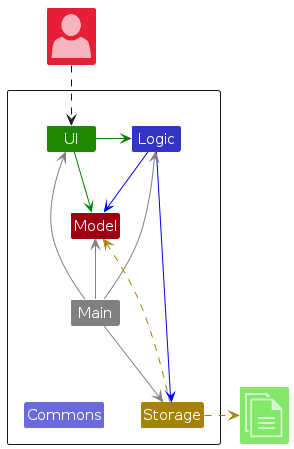
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete n/John.
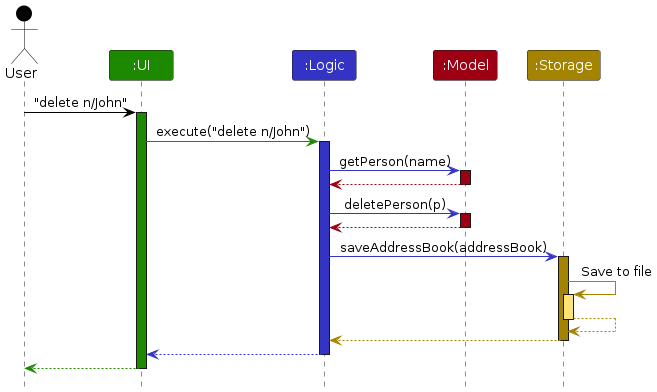
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
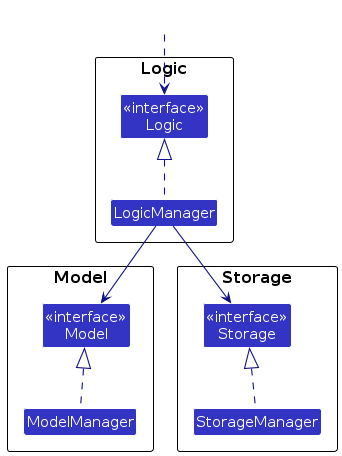
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
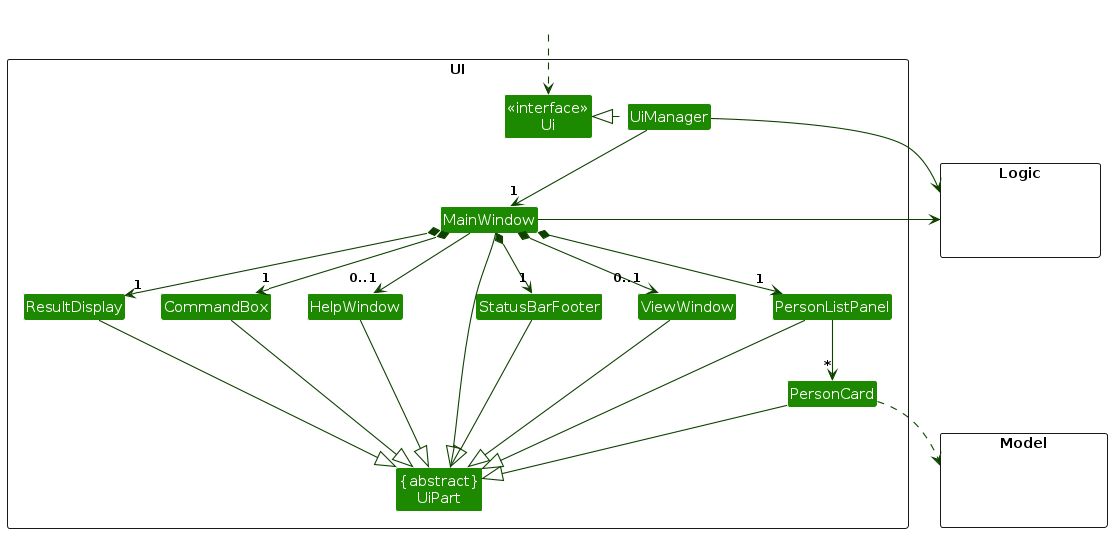
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
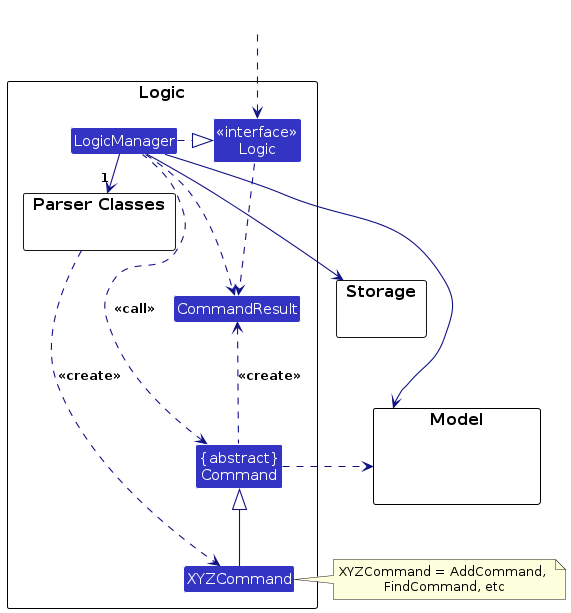
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete n/John") API call as an example.
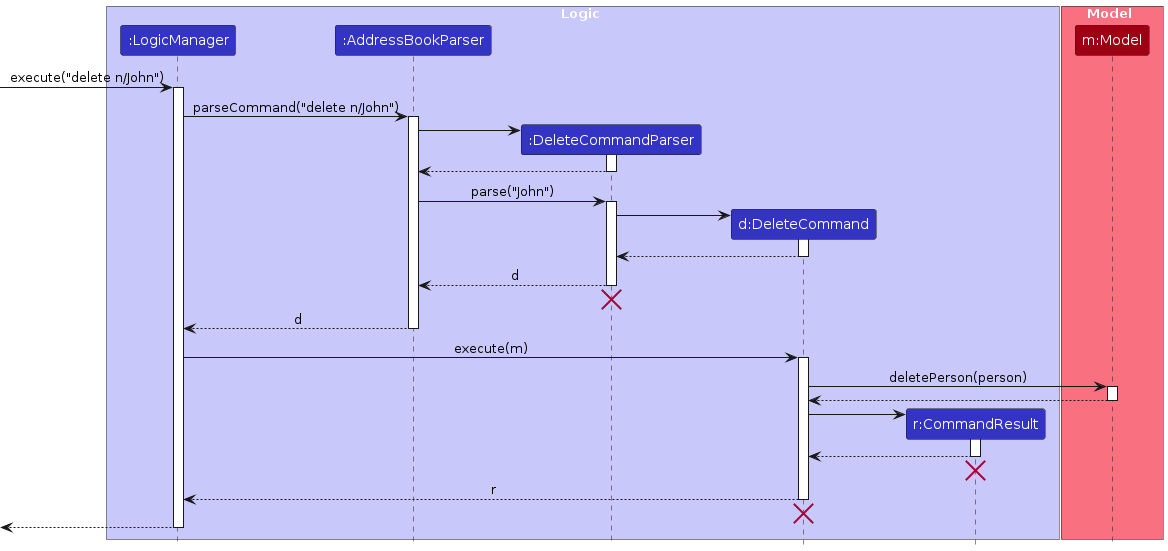
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
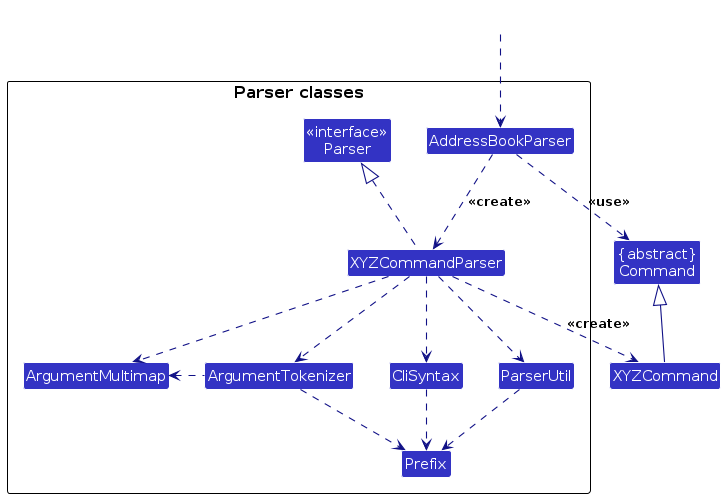
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
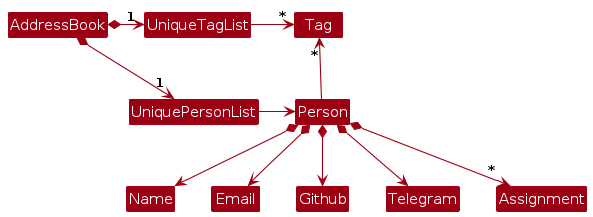
Model component
API : Model.java
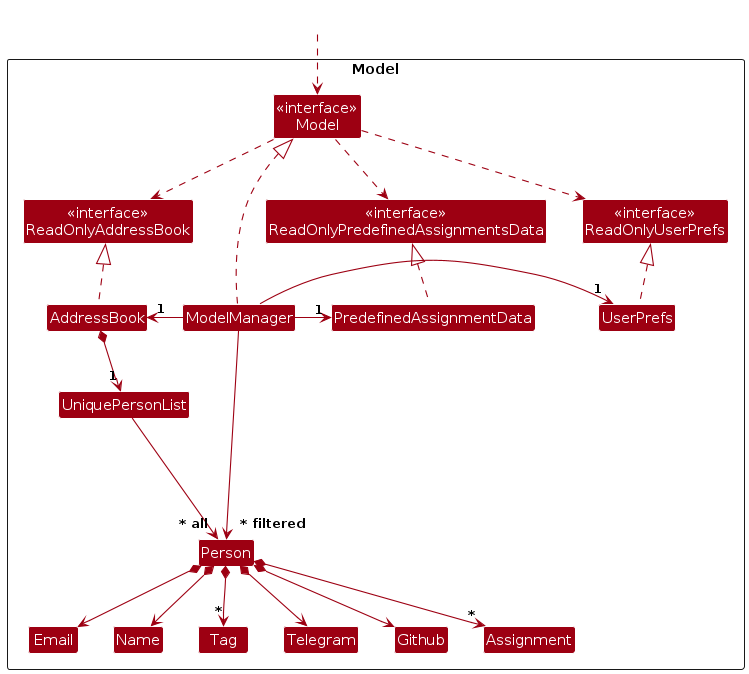
The Model component,
- stores the KonTActs data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Note: An alternative (arguably, a more OOP) model is given below. It has a Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.
Storage component
API : Storage.java
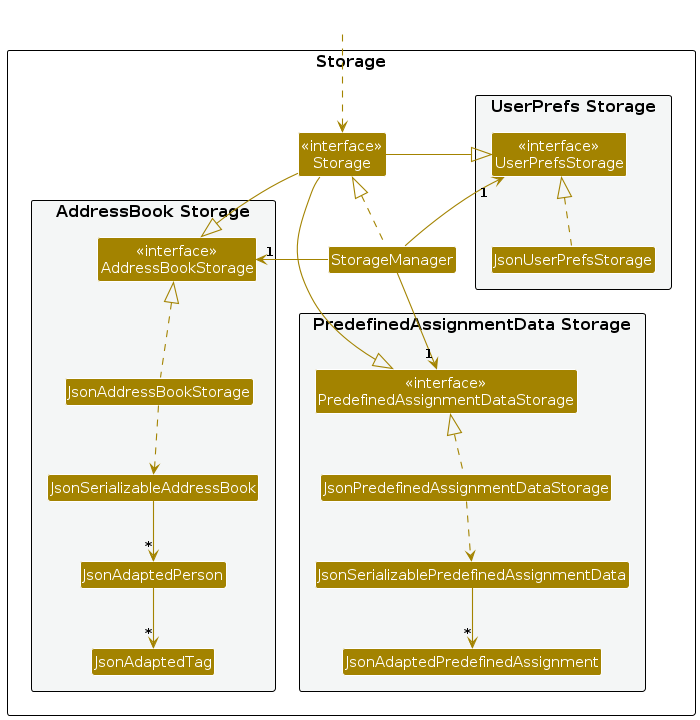
The Storage component,
- can save both KonTActs data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Add contacts
Overview
The add command allows user to add students' contact into KonTActs.
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the logic component handles the user input.
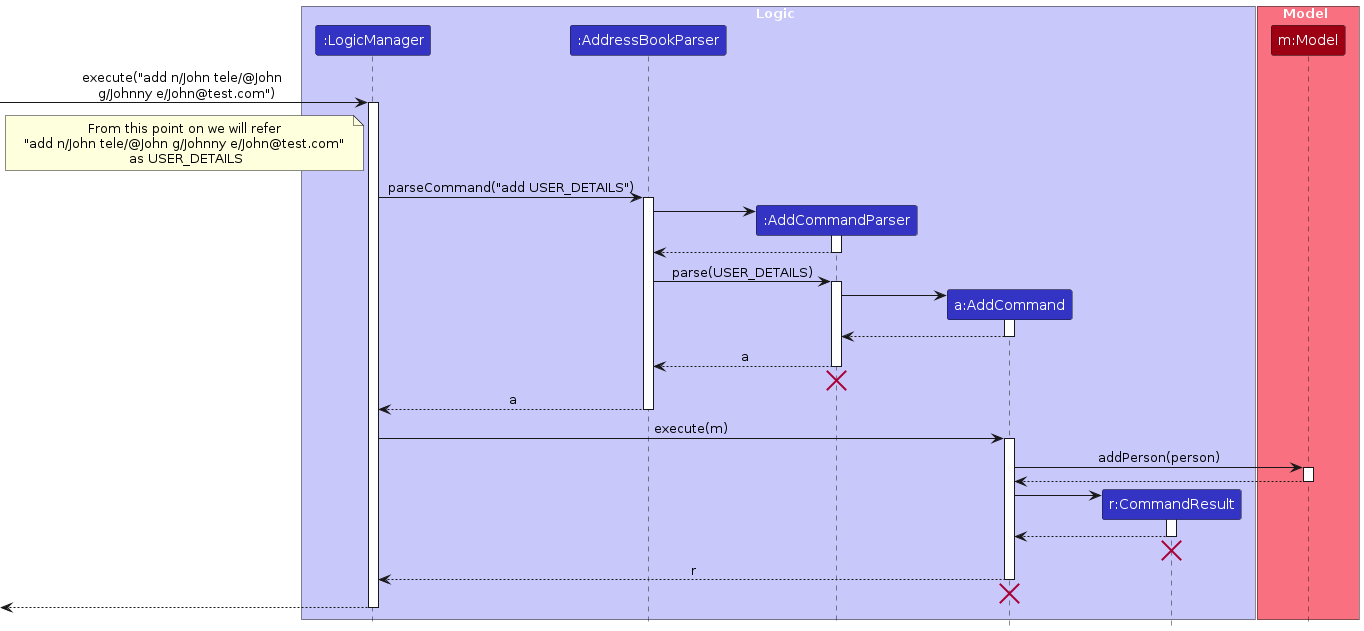
Note: While the diagram shows the lifeline of objects even after their deletion, this is a limitattion of plantUML.
Details
- The user inputs "add n/John tele/@John g/Johnny e/John@test.com". (Not shown in diagram)
- The
LogicManagerobject will be called toexecutethe input. - The
AddressBookParserwill identify the type of command isAddCommand, before creating aAddCommandParserto parse the details. - The
AddCommandParserwillparsetheUSER_DETAILSbefore creating aAddCommand. - The new
AddCommandwill be returned toLogicManager. - The
LogicManagerwill then callsexectuteonAddCommandwhile providing the model. - This causes the
AddCommandto call theaddPersonmethod of model, adding the person to the model. - A
CommandResultobject is subsequently created which indicates the success ofAddCommand.
Example Usage
- User inputs the command "add n/Tom tele/@Tom g/Tommy e/Tom@test.com".
- KonTActs will create a contact of Tom with the given details before adding it to the contact list.
- The contact is then displayed in the UI, along with a success message.
Add Grade implementation
Logic:
AddGradeCommand.javaAddGradeCommandParser.java
The addGrade command is used by KonTActs to add an assignment and grade to a contact.
The added assignments and grades uses HashMap to store the assignments and grades in each person object.
This is illustrated in the activity diagram below:
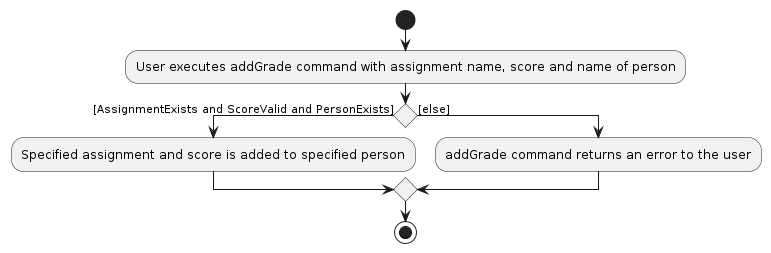
- addGrade checks whether the assignment exists in the database, if the score is valid and if the person exists in the contacts.
- If the conditions are satisfied, the assignment is added to the
HashMapin the person object which stores all the added assignments of that person.
MarkCommand
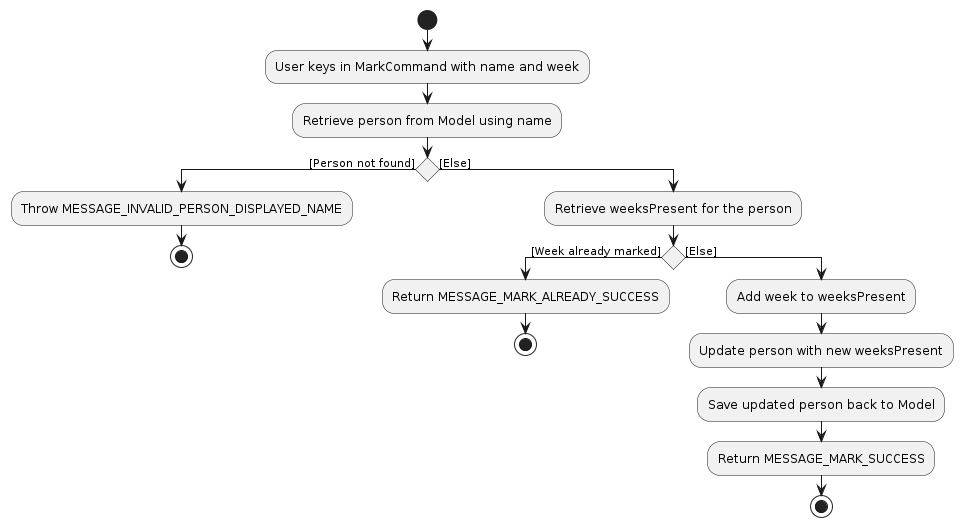
- The
MarkCommandis used by KonTActs to allow TAs to mark the attendance for a student. - It follows the activity diagram as shown above where it first checks if the person exists.
- If the person exists, it will check if the weeksPresent contains the week to be marked.
- If the weeksPresent does not contain the week to be marked yet, it will add it in and return a success message. Else it will throw a mark already success message to tell the TA that the attendance for the TA for that week has been marked.
Example Usage
- User inputs the command "mark n/John Doe w/1".
- KonTActs will set the week 1 attendance for John Doe to be true.
- The update is then displayed in the UI, along with a success message.
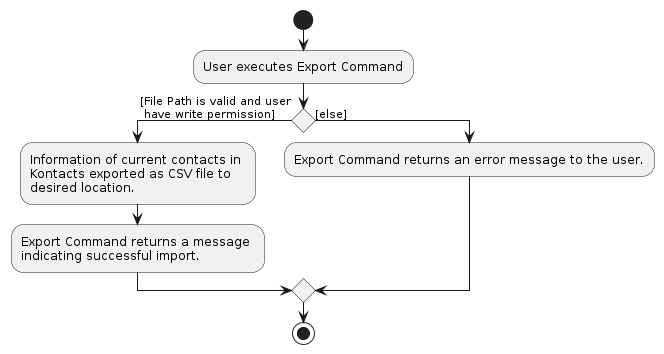
Export Command implementation
API Export.java
The ExportCommand is used by KonTActs to allow users to export contact data as a CSV file that can be
easily shared or imported. The ExportCommand operates on the existing list of contacts and
exports them to the specified file location.
- The command validates the file path and handle any errors during the export process.
- Error message will be displayed if any errors are encountered.
- ExportCommand retrieves all contact data from KonTActs and formats the data it into a CSV file.
- After the export is completed (file is saved at desired location), a confirmation message will be displayed.
A visual representation is shown below of how a typical user might use the ExportCommand,
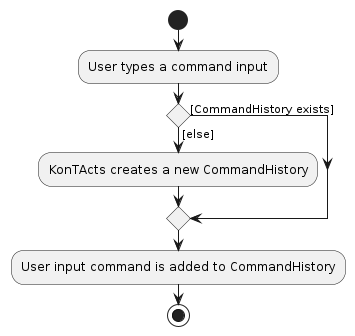
Command History implementation
API : CommandHistory.java
The CommandHistory is used by KonTActs to allow users to navigate and retrieve previous inputted commands. It follows a singleton pattern where only a single instance can be created.
CommandHistorymakes use of anArrayListto store the commands of the current user session.- The
ArrayListis destroyed at the end of the program and a new one will be created at the start of every session of KonTActs. - An
indexpoints to the current command displayed in the command box of the Graphical user interface (GUI).
When a user enters a command,
- If an existing
CommandHistoryinstance already exists, then the command will be added to it - Else, a new
CommandHistoryinstance will be instantiated and the command will be added to it
This is illustrated in the activity diagram below:
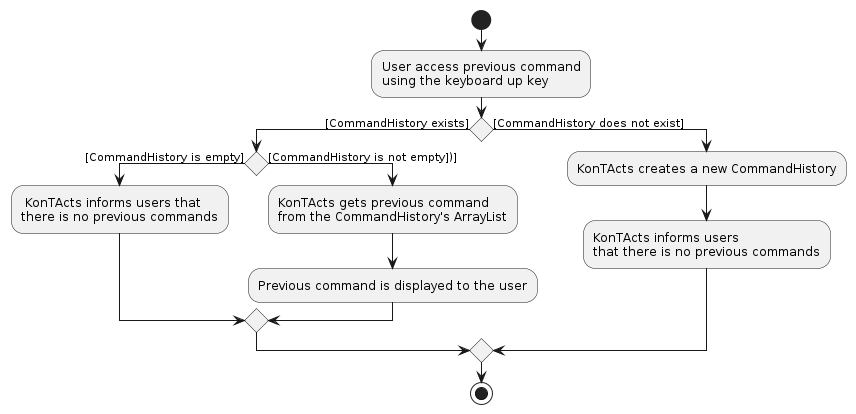
When a user retrieves a command that was previously executed using ↑ or ↓,
CommandHistoryinstance first checks if there are fields in theArrayListof theCommandHistoryinstance.CommandHistoryinstance then checks for the correctindex. (i.e. Theindexis valid when it is between 0 and the size of theArrayList).
If both conditions are satisfied, the ArrayList is accessed with the index and the command string (that was previously entered) will be returned and displayed on the command box of the GUI.
A visual representation is shown below of how a typical user might use the CommandHistory,
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- has a need to manage a significant number of contacts
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: manage contacts faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a/an … | I want to … | So that … |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | CS2030S TA | store student's github username | I can easily reference them when grading assignments. |
* * * | user | add the student's contact number | I can easily reference them when I need to contact my students. |
* * * | CS2030S TA | add the contact details of other TAs | I can quickly reach out for help or collaboration. |
* * * | CS2030S TA | add contact details of professors | I can easily reach them for guidance or to pass on important information. |
* * * | CS2030S TA | delete contacts easily | I dont clutter the list with unwanted contacts. |
* * * | CS2030S TA | store the grades and progress of my students | I can keep track of which of my students need more guidance and follow up. |
* * * | CS2030S TA | store student's telegram username | I can easily reference them and contact them when needed to. |
* * * | CS2030S TA | see the student's MC or reasoning when they do not turn up for lessons | I can create make up lessons / check up on them. |
* * | CS2030S TA | have a function to hide the details of students that I do not need | I can only the the information that I want to see. |
* * | CS2030S TA | view the last modification date of student contact details | I can confirm the accuracy and recency of the information stored. |
* * | CS2030S TA | create contacts with optional fields | I can resepct the privacy of my students. |
* | CS2030S TA | search for a student’s GitHub username | I can quickly access their repository for grading and feedback. |
* | potential user | see the application populated with sample data | I can see how the app looks like when it is in use. |
* | CS2030S TA | put the contacts into different tabs | I can easily navigate between different types of contacts. |
* | CS2030S TA | use the command line interface to search for contacts | I can integrate the tool smoothly into my existing workflow. |
* | CS2030S TA | search for the contact details of professors/ other TAs | I can quickly contact them for help if needed. |
* | CS2030S TA | find my students house in time | I can offer them help in times of crisis. |
* | CS2030S TA | organise the contact of my students | I can view the details of each student with greater ease. |
* | CS2030S TA | import student contact information from a file | I can easily transfer data between devices. |
* | CS2030S TA | export student contact information to a file | I can backup or share contact details with other TAs or professors if needed. |
* | CS2030S TA | flag specific students for follow-up | I can easily identify students who may need additional support or guidance. |
* | CS2030S TA | choose to sort my students | I can group students based on their proficiency. |
* | CS2030S TA | filter the contact details that is shown | I can easily find the information of a particular group. |
* | CS2030S TA | filter contacts based on a certain criteria | I can access a specific subset of students that I want. |
* | CS2030S TA | tag students with custom labels | I can categorize students based on their progress or needs. |
* | CS2030S TA | use the command line to access my students work | have their work and contact and tags all tied together in one smooth workflow. |
* | experienced user | create shortcuts for commands that I use frequently | I can access the frequently used information quickly. |
* | new user | use a help function to check what this app offers | I can easily have the details of the commands to use in my fingertips. |
* | CS2030S TA | create automatic flags to indicate if a student's work is marked | I can monitor grading deadlines so that I can stay on top of my responsibilities without missing any critical dates. |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the KonTActs and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC01 - Add contacts
MSS
User chooses to add a contact, providing the information that is required.
KonTActs adds the new contact and indicates success.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1 - 1a2 are repeated until input entered is correct.
Use cases resume from step 2.
Use case: UC02 - Delete contacts
Precondition
- The contact that the user wants to delete exists.
MSS
User chooses to delete a contact.
KonTActs deletes the contact and indicates success.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1 - 1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC03 - Add grades of students
Precondition
- The student that the user wants to add grades exists.
- The assignment that the user wants to add a grade to exists.
MSS
User chooses to add grades for a student, providing the assignment details and grade.
KonTActs updates the grade of the student and indicates success.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC04 - List contacts
MSS
User chooses to view the entire contact list.
KonTActs displays the full list of contacts.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC05 - Edit contacts
MSS
User chooses to edit a contact’s detail, providing the updated details.
KonTActs updates the details of the contact and indicates success.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects that the contact provided does not exist.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
1b. KonTActs detects that the new details provided is invalid.
1b1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1b2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1b1-1b2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC06 - Filter Contact List
MSS
User chooses to filter the contact list, providing the filter criteria.
KonTActs filters the contact list and displays the filtered list.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1a2. Users enter a new input.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC07 - Export contacts
Precondition
User must have permission to write to the provided path.
User must have enough storage to store the output file.
MSS
User chooses to export the contact list, providing the file path.
KonTActs exports the contact list in CSV format and indicates success.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC08 - Request for help
MSS
User inputs help command.
KonTActs shows a help page.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC09 - Tag students with custom labels
Precondition
- The student that the user wants to tag is in KonTActs.
MSS
User chooses to tag a student.
KonTActs requests for details of the student alongside the tag to label the student.
User enters the requested details.
KonTActs tags the student with the suggested label.
Use case ends.
Extensions
3a. KonTActs detects an error in the entered data.
3a1. KonTActs request for the correct data.
3a2. User enters new data.
Steps 3a1-3a2 are repeated until the data entered are correct.
Use case resumes from step 4.
Use case: UC10 - Import contacts from CSV file
Precondition
- The file is in CSV format and ends with
.csv. - The file contains valid data of at least 1 person.
- The header of the file is in the required sequence.
- Current user have permissions to access and read the file.
MSS
User chooses to import the contact list, providing the desired file path.
KonTActs imports the contact list from the specified file path and indicates successful import.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects the file provided is invalid.
1a1. KonTActs request for the correct file path.
1a2. User provides a new file path.
Steps 1a1 - 1a2 are repeated until KonTActs is able to import contacts from the file.
Use case resumes from step 2.
1b. KonTActs detects invalid content in CSV file.
1b1. KonTActs request for the correct file path.
1b2. User provides a new file path or update their CSV file
Steps 1b1 - 1b2 are repeated until KonTActs is able to import contacts from the file.
Use case resumes from step 1.
*a. At any time, User chooses to cancel the import.
*a1. KonTActs stops the import.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC11 - Sort Contact List
MSS
User chooses to sort the contact list, providing the sort criteria.
KonTActs sorts the contact list and displays the sorted list.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs requests for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: UC12 - Open student's GitHub page
Precondition
- The user have set permissions to allow browser to be opened from external applications.
MSS
User chooses to open the Github page of a student.
KonTActs opens the Github page on the user's default browser.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. KonTActs detects an error in the input.
1a1. KonTActs requests for the correct input.
1a2. User enters a new input.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the input entered is correct.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 17 or above installed.
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 persons without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Commands should be easy to remember.
- Ui should be easy to navigate and intuitive.
- KonTActs should be easy to use for new users.
- The system should work on both 32 bit and 64 bit environments.
- Contact details are securely stored.
- The application should have an uptime of at least 99.9% to ensure constant availability for users.
- The application should automatically save data after every change to avoid data loss in case of a crash.
- There should be proper documentation for the code and application usage to assist developers in future updates.
- Error messages should be descriptive, providing users with clear guidance on how to resolve the issue.
- Searching for or filtering contacts should take less than 5 seconds.
- Stored contacts are persisted between sessions.
Glossary
Contact: An individual (e.g. student) stored in the system, typically having details regarding them such as their name, github username and etc.
Easy to use for new users: Intuitive commands that are easy to understand and UI that is easy to navigate.
Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS.
Average typing speed: About 40 words per minute.
Uptime: The system should be operational during that period of time.
Between sessions: Every opening and closing of the application.
Proper documentation: A detailed user and developer guide which helps future users and developers to understand and use the code.
Typical usage: Normal or expected usage patterns of the application, such as the frequency of adding, deleting, or viewing contacts during everyday use.
Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Team member count: 5
- Implement commands to add/edit assignment details: Currently, one has to edit the
kontacts.jsonfile manually to add or remove assignment details. This could be an issue as the information keyed in may be incorrect. We are planning to create commands which can add/edit assignment details (such as assignment nameEx04and its respectivemaxGradefields) to theassignment.jsonfile. This is to make the adding/editing of new assignments easier and prevent wrong information being entered. - Include validation for Telegram ID: Currently, KonTActs does not check for the Telegram ID's length despite it not being a valid username in Telegram. In future updates, we are planning to provide proper Telegram ID validation to prevent users from inputting usernames that are not accepted by Telegram.
- Add flexibility to attendance: Currently, the maximum number of weeks that can be inputted is 14 since there are 14 weeks in a semester (from week 0 to week 13). However, it is possible that the user would want to use it for a different amount of weeks such as during special terms. Thus, we plan on incorporating commands to edit the start or end week of the attendance.
- Improve UI of Result Display box: Currently, the Result Display only shows three lines of message to the user. However, some of the details require more than three lines to be seen. We plan to improve the UI such that users are able to adjust the size of the Result Display box to display more information.
- Improve scroll-ability of application: Currently, when there is a long tag, and the View Window is closed, the scroll of the application does not work. Although there is a workaround to it, it is not efficient and prevents fast usage. So, we plan on editing the View Window and the Main Window to make it more user-friendly.
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
Initial launch
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
Saving window preferences
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
Deleting a person
Deleting a person while all persons are being shown
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. Multiple persons in the list.Test case:
delete name/John Doe
Expected: Deletes the contact named John Doe. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete n/ABC,...(where nameABCdoes not exist in the list)
Expected: An error message redirecting to the correct format.
Adding a person
Add a person to KonTActs
Test case:
add name/John Doe email/johndoe@test.com telegram/@johndoe github/johndoe
Expected: Contact with nameJohn Doeis added to the list. Details of the added contact shown in the status message.Test case:
add name/John Do3 email/johndo3@test.com telegram/johndoe github/john#$doeExpected: No person is added. Error details shown in the status message.Other incorrect add commands to try:
add,add ...(where...is any pair of prefix and value)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Editing a contact
- Editing a contact field that is shown in the list
Test case:
edit 1 name/John TanExpected: Contact shown at index 1 has name edited toJohn Tan. Details shown in status message.Test case:
edit 0 name/John TanExpected: No contact is edited. Details of error shown in status message.Other incorrect edit commands to try:
edit -1 name/John Tan,edit x name/John Tan(wherexis a number that is not in the shown list) Expected: Similar to previous
Adding grade to a person
- Add grades to a person
Prerequisites:
assignment.jsonindatawith the following content:
{ "assignments" : [ { "name": "Ex01", "maxScore": 5 },{ "name": "Ex02", "maxScore": 5 },{ "name": "Ex03", "maxScore": 5 },{ "name": "Ex04", "maxScore": 5 } ] }Test case:
addGrade n/John Doe a/Ex04 s/5
Expected: AssignmentEx04with score5is added toJohn Doe. Details of the added grade shown in the status message.Test case:
addGrade/John Doe a/Ex05 s/5
Expected: No grade is added to John Doe. Details of the error message is shown in the status message.Other incorrect add grade commands to try:
addGrade,addGrade s/x(wherexis not a number orxis bigger than the max value of the assignment)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Removing grade from a person
- Remove grade from a person
Prerequisites: Contact
John Doewith grades(assignment name,score)Ex01,5andEx02,3added.Test case:
removeGrade n/John Doe a/Ex01
Expected: AssignmentEx01is removed fromJohn Doe. Details shown in the status message.Test case:
removeGrade/John Doe a/Ex05 s/5
Expected: No grade is removed from John Doe. Details of the error message is shown in the status message.Other incorrect remove grade commands to try:
removeGrade,removeGrade a/x(wherexis any value)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Marking attendance of a person
- Marking attendance of a person in KonTActs
Test case:
mark n/John Doe w/5
Expected:John Doeis marked as present for week 5. Details of the marked week is shown in status message and the list.Test case:
mark n/John Doe w/999
Expected: Attendance not marked forJohn Doe. Details of the error is shown in the status message.Other incorrect mark commands to try:
mark,mark n/JohnDoe
Expected: Similar to previous.
Unmarking attendance of a person
- Unmarking attendance of a person in KonTActs
Test case:
umark n/John Doe w/5
Expected:John Doeis marked as absent for week 5. Details of the unmarked week is shown in status message and the list.Test case:
unmark n/John Doe w/999
Expected: No attendance unmarked forJohn Doe.Other incorrect unmark commands to try:
unmark,unmark n/JohnDoe
Expected: Similar to previous.
Import CSV
- Importing list of persons from a CSV file.
Prerequisites:
example.csvindata"Name","Email","Telegram","Tags","Github","Assignments","WeeksPresent" "Alex Yeoh","alexyeoh@example.com","@alex","[friends]","Alex","","" "Bernice Yu","berniceyu@example.com","@bernice","[colleagues],[friends]","Bernice","","" "Charlotte Oliveiro","charlotte@example.com","@charlotte","[neighbours]","Charlotte","","" "David Li","lidavid@example.com","@david","[family]","david","","" "Irfan Ibrahim","irfan@example.com","@irfan","[classmates]","Irfan","","" "Roy Balakrishnan","royb@example.com","@roy","[colleagues]","Roy","",""Test case:
import path/data/example.csvExpected:example.csvis imported.Test case:
import path/data/x.csvExpected: No data is imported. Details of the error is shown in status message.Other incorrect import commands to try:
import,import path/
Expected: Similar to previous.
Export CSV
- Export list of persons to a CSV file.
Test case:
export path/data/example.csvExpected:example.csvis exported. Details shown in status message.Test case:
exportExpected: No data is exported. Details of the error is shown in status message.Other incorrect export commands to try:
export path/
Expected: Similar to previous.
Filtering for list of persons
- Filter for persons based on tag
Test case:
filter t/friends t/colleague. Expected: List shows contacts with tagsfriendsorcolleague.Test case:
filterExpected: No change in list. Details of error shown in status message.Other incorrect filter commands to try:
filter s/,filter t/
Expected: Similar to previous.
Sorting list of persons
- Sort contacts based on field(
github, name, telegram or reset) of given personTest case:
sort name order/ascExpected: List sorted based on name in ascending order. Details shown in status message.Test case:
sort email order/ascExpected: List is not sorted. Details of error shown in status message.Other incorrect sort commands to try:
sort order/asc,sort order/descExpected: Similar to previous.
Finding persons
- Finding persons based on name.
Prerequisite:
John Doe,Alice, andCindyexists in KonTActs.Test case:
find john doe aliceExpected:John DoeandAliceis found and revealed in the list. Details shown in status message.Test case:
findExpected: No change. Details of error shown in status message.
Viewing a person
- Viewing a detailed info person
Test case:
view n/John DoeExpected: View window forJohn Doeappears. Details shown in status message.Test case:
view n/Expected: No view window appears. Details of error shown in status message.Other incorrect view commands to try:
view nExpected: Similar to previous.
Launching Github page of person
- Open browser and navigate to person's Github page on command
Prerequisite:
John Doewith Github usernamejohndoeexists.Test case:
github n/John DoeExpected: Github page ofJohn Doeis opened in browser. Details is shown in status message.
Listing contacts
- List all contacts in KonTActs
- Test case:
listExpected: List of contacts shown. Details shown in status message.
- Test case:
Clearing contacts
- Removing all contacts in KonTActs
- Test case:
clearExpected: All contacts are removed from KonTActs. Details is shown in status message.
- Test case:
Viewing help
- View help of every command
- Test case:
helpExpected: A help window is shown with link to documentation.
- Test case:
Exiting application
- Test case:
exitExpected: Application exits after command.
Saving data
Dealing with missing files
Test case: Remove
.jsonfromdata.
Expected: A sample list of KonTActs will be loaded.Test case: Add an invalid value to
kontacts.json. e.g."email":1
Expected: No contacts will be loaded.